In 2010, a group of scientists from the United Kingdom’s Independent Scientific Committee on Drugs, including two invited specialists, met to rank the harm levels of 20 drugs. Their findings defied expectation, and now – over a decade later – their predictions appear to be more accurate than ever.
Read on to learn where marijuana falls in the mix (and why alcohol may be more dangerous than heroin!).
Drug Harm Study: Background
Published in The Lancet, one the most well respected peer-reviewed scientific journals, the 2010 drug harm study used an an advanced multi-criteria decision analysis (MCDA) approach. Similar technology has been successfully applied to facilitate decision-making in complex scenarios such as developing appraisal policies for disposal of nuclear waste.
Translation?
The scientific model employed in the present study is incredibly trustworthy!
Before beginning their analysis, scientists identified 16 harm criteria. According to the study authors:
Nine relate to the harms that a drug produces in the individual and seven to the harms to others both in the U.K. and overseas.
These harms are clustered into five subgroups representing physical, psychological, and social harms.
Drugs were scored with points out of 100, with 100 assigned to the most harmful drug on a specific criterion. Zero indicated no harm.
What Drugs Are Most Harmful?
The study’s results made global headlines when they were announced:
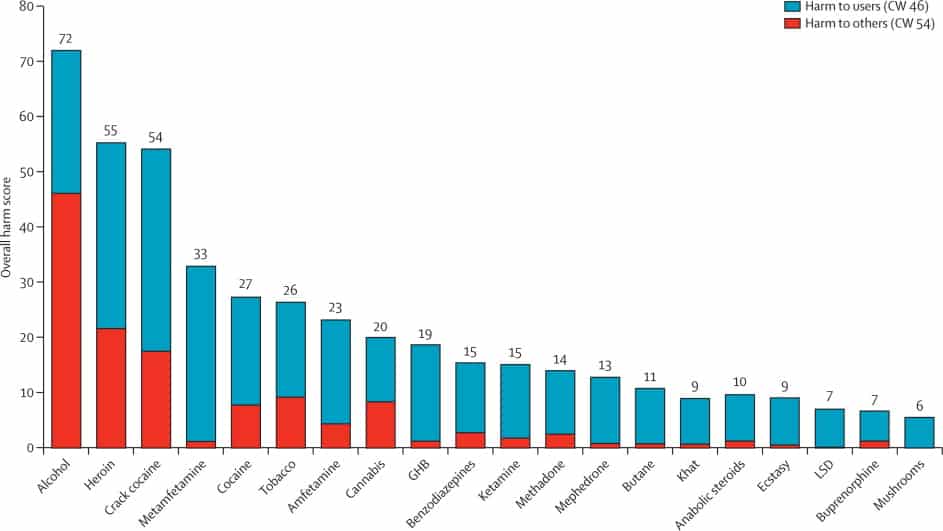
The most harmful drugs to users were heroin (part score 34), crack cocaine (37), and metamfetamine (32), whereas the most harmful to others were alcohol (46), crack cocaine (17), and heroin (21).
When the two part-scores were combined, alcohol was the most harmful drug followed by heroin and crack cocaine.
Marijuana’s combined score was 20 – less than one-third of alcohol’s cumulative score of 72!
The chart below illustrates harm to users (blue), harm to others (red), and combined harm:
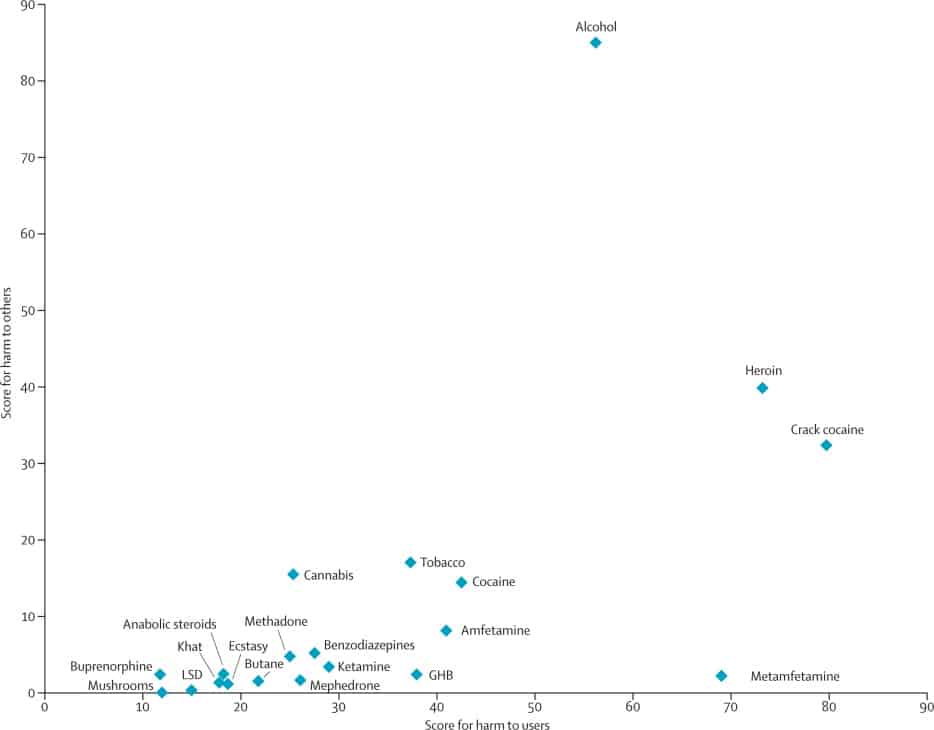
This second chart shows the same data in a two-dimensional graph so that the relative contribution to both types of harm can be seen clearly:
According to researchers:
The most harmful drug to others was alcohol by a wide margin, whereas the most harmful drug to users was crack cocaine followed closely by heroin.
Metamfetamine was next most harmful to users, but it was of little comparative harm to others.
All the remaining drugs were less harmful either to users or to others, or both, than were alcohol, heroin, and crack cocaine.
Perhaps most interestingly, this third chart shows the contributions that the part scores make on each criterion to the total score of each drug:
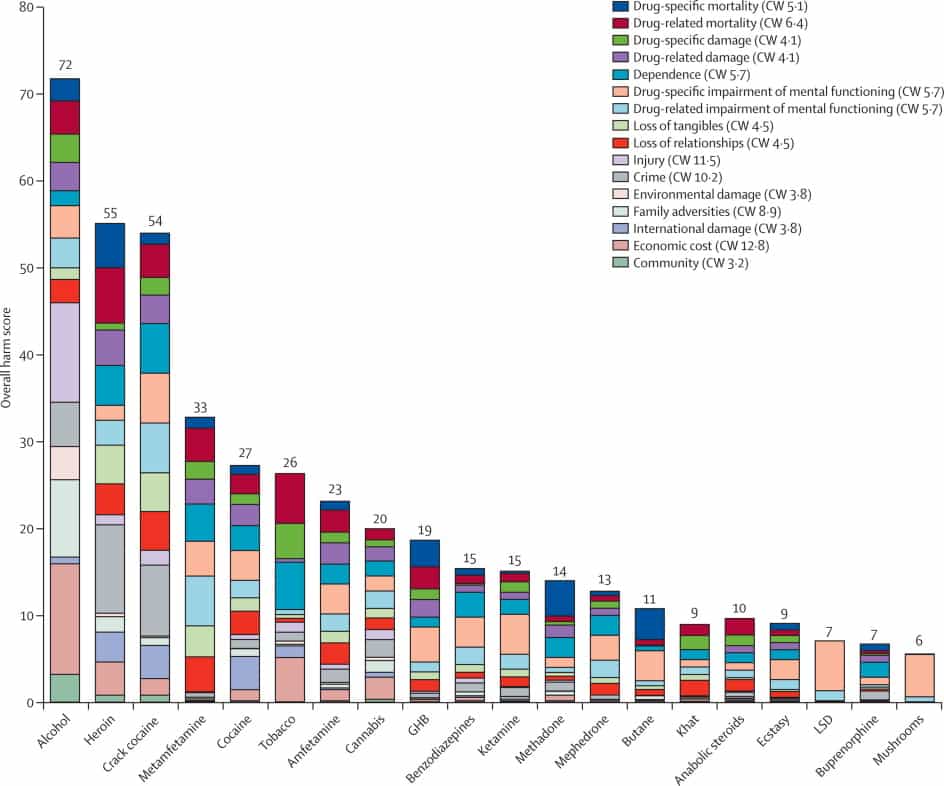
Alcohol, with an overall score of 72 (over three times that of marijuana!), was judged to be most harmful, followed by heroin at 55, then crack cocaine with a score of 54. Only eight drugs scored, overall, 20 points or more. Drug-specific mortality was a substantial contributor to five of the drugs (alcohol, heroin, γ hydroxybutyric acid [GHB], methadone, and butane), whereas economic cost contributed heavily to alcohol, heroin, tobacco, and cannabis.
What Scientists Say
Speaking about the study’s results in context of the United Kingdom’s drug scheduling program, the authors write:
Our findings lend support to previous work in the U.K. and the Netherlands, confirming that the present drug classification systems have little relation to the evidence of harm. They also accord with the conclusions of previous expert reports, that aggressively targeting alcohol harms is a valid and necessary public health strategy.
Now, over ten years later, as more and more research demonstrates the benefits of marijuana – and the comparative harm of the other drugs surveyed – these findings serve as a reminder that marijuana’s Schedule I classification in the United States is not only out of sync with scientific data: It stands in direct opposition to research from some of the most well respected experts in the world.





